Analysis-1(Land Skin Temperature +5℃)
- 2019년 5월 28일
- 2분 분량
최종 수정일: 2019년 6월 3일
[initial state] [land skin temperature +5℃]
land: 298K, sea: 293K land: 303K, sea: 293K
- 10:00 AM
When we raise the temperature of the land by 5K, we can see that the wind of right graph is bigger at 10:00 AM.
We can see that the right land temperature is high.
- 12:00 PM
At 12:00 PM, the sun rises and the sea breeze is stronger.
- 2:00 PM ~ 3:00 PM
[u-wind, 2:00 PM]
[u-wind, 3:00 PM]
We wondered over time that there would be several masses of wind in the land. Therefore, we checked the solar radiation and cloud to find out the cause.
[Cloud, 2:00 PM]
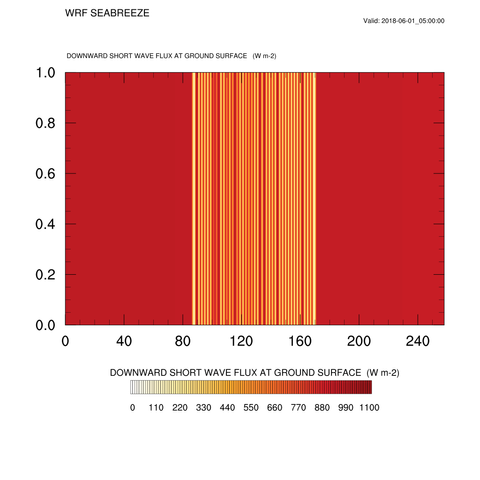
[solar radiation, 2:00 PM]
Clouds first forms at 2:00 PM as the sea breeze becomes stronger. These clouds are more likely to be formed when +5K has been applied to the land. And the clouds affect the solar radiation quantity. we can see the solar radiation quantity's definitely drop where the clouds are located.
[Temperature, 2:00 PM]
[Temperature, 3:00 PM]
Looking at the 3:00 PM temperature, there is a slight decrease in temperature compared to the previous time, which corresponds to the pattern of solar radiation at 2:00 PM.
-4:00 PM
At 4:00 PM, we can see the graphs of solar radiation are lighter than the previous time. And if we look at the u-wind graph at 4:00 PM, we can see that the wind direction and intensity vary in the area of the land, unlike the sea section. We saw that the land area had this aspect because of the differential heating of the land caused by earlier clouds.
- 7:00 PM
As the sun goes down, the solar radiation decreases and the wind's turbulence decreases, so we can see the amount of clouds decrease.
- 8:00 PM
There's no solar radiation at 8:00 PM
The 5K increase in land temperature starts the transition to the wind direction faster than the initial state.
- 9:00 PM
After one hour, the initial state also begins to change the direction of the wind.
- 12:00 AM
We can see that the land temperature on the right is higher when the land breeze continues. So it can be predicted that the right side of the wind will last shorter.
- 6:00 AM
As the sun rises at six, a little red light begins to appear on the temperature graph as the sun rises.
- 7:00 AM
Temperatures that have risen in the previous time have affected the change from the land breeze to the sea breeze. The transition takes place and ends.
[Conclusion]
We analyzed the sea breeze through temperature, solar radiation, and clouds.
Higher land temperatures created more clouds, resulting in more differential heating, and the strength of the sea breeze was stronger under the influence of higher temperatures.
[Question]
We expected longer periods of sea breeze as the land temperature rises.
But the actual results did not.
We thought that this was the result of different temperature ranges between land and sea, so we conducted the experiment in analysis-2 with the same temperature range.


























































































댓글